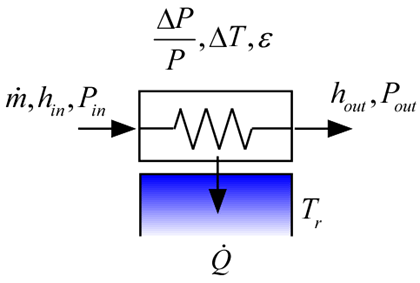
HeatExchanger1_CL

The procedure HeatExchanger1_CL models a heat exchanger in which a fluid is interacting with a reservoir (i.e., a source or sink that has infinite capacitance). The approach temperature difference is specified. This function works with real fluids, ideal gas, incompressible, or brines.
Inputs:
F$: fluid string identifier
C: Concentration (%) - note that this is only necessary if the fluid is a brine; otherwise set C=0
m_dot: mass flow rate (kg/s or lbm/hr)
h_in: inlet specific enthalpy (J/kg, kJ/kg, or Btu/lbm)
P_in: inlet pressure (bar, atm, Pa, kPa, MPa)
T_r: temperature of the reservoir (K, C, R, or F)
DT: approach temperature difference (K, C, R, or F)
DPoverP: pressure drop normalized by absolute pressure (-)
Outputs:
h_out: outlet specific enthalpy (J/kg, kJ/kg, or Btu/lbm)
P_out: outlet pressure (bar, atm, Pa, kPa, MPa)
Q_dot: heat transfer rate (W, kW or Btu/hr)
into device if T_r>T_in
out of device if T_r<T_in
eff: effectiveness (-)
Example 1:
$Load Component Library
$UnitSystem SI Mass J K Pa
$Load Incompressible
$VarInfo h_in units=J/kg
$VarInfo h_out units=J/kg
$VarInfo P_out units=Pa
$VarInfo Q_dot units=W
F$='DowTherm_Q'
C=20 [%]
m_dot=0.01 [kg/s]
T_in=380 [K]
P_in=4e6 [Pa]
h_in=enthalpy(F$,T=T_in,P=P_in)
T_r=300 [K]
DT=10 [K]
DPoverP=0.01 [-]
Call heatexchanger1_cl(F$, 0, m_dot, h_in, P_in, T_r, DT, DPoverP: h_out, P_out, Q_dot, eff)
{Solution:
h_out = 125990 J/kg
P_out = 3.96-0e6 Pa
Q_dot = 1274 W
eff = 0.8827}
Example 2:
$Load Component LIbrary
$UnitSystem SI Mass J K Pa
$VarInfo h_in units=J/kg
$VarInfo h_out units=J/kg
$VarInfo P_out units=Pa
$VarInfo Q_dot units=W
F$='EG'
C=20 [%]
m_dot=0.01 [kg/s]
T_in=380 [K]
P_in=4e6 [Pa]
h_in=enthalpy(F$, T=T_in, C=C, P=P_in)
T_r=300 [K]
DT=10 [K]
DPoverP=0.01 [-]
Call heatexchanger1_cl(F$, C, m_dot, h_in, P_in, T_r, DT, DPoverP: h_out, P_out, Q_dot, eff)
{Solution:
h_out = 119770 J/kg
P_out = 3.960e6 Pa
Q_dot = 2793 W
eff = 0.8770}