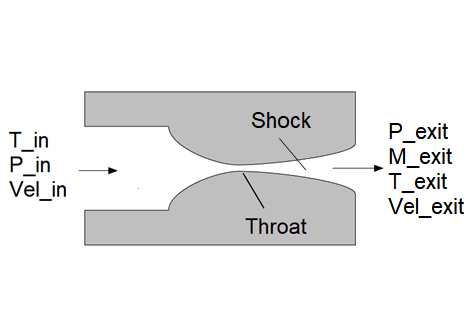
CDNozzle2_CL

CDNozzle2_CL provides a model of a converging-diverging (CD) nozzle in which a normal shock occurs between the nozzle throat and outlet. This model assumes isentropic flow through the throat to the location of the shock. Isentropic flow also occurs downstream of the shock to the outlet. The fluid can be any ideal gas or real fluid within the EES database. However in either case, the model assumes ideal gas behavior of the fluid. The cross-sectional area at the location of the shock, A_s, is provided as an input in order to calculate the exit pressure, temperature and velocity. It is also possible to specify the exit pressure in order to calculate A_s.
CALL CDNozzle2_CL(Gas$,T_in, P_in, Vel_in, A_throat, A_exit, A_s : P_exit, M_exit, T_exit, Vel_exit, P_crit, P_design)
Inputs:
Gas$ Name of a gas in the EES database
T_in: inlet temperature (C, K, F, R)
P_in: inlet pressure (bar, atm, Pa, kPa, MPa)
Vel_in: inlet velocity (m/s, ft/s)
A_throat area of the nozzle throat (m^2, ft^2)
A_exit area of the nozzle exit or specified position along the flow length (m^2, ft^2)
M_guess guess for the outlet Mach number. Use a value <1 for subsonic flow and >1 for supersonic flow
Type$ either 'ideal' or 'real'; a real gas analysis occurs if Gas$ is a real fluid and Type$='real'; otherwise an ideal gas analysis is provided.
Outputs:
P_exit: nozzle exit pressure (bar, atm, Pa, kPa, MPa)
M_exit Mach number at the exit
T_exit: nozzle exit temperature (C, K, F, R
Vel_exit: velocity at the exit(m/s, ft/s)
P_crit: critical pressure (i.e., the pressure at the nozzle throat) (bar, atm, Pa, kPa, MPa)
P_design: design pressure (i.e., the pressure at the exit if the gas is expanded isentropically with no shock) (bar, atm, Pa, kPa, MPa)
Example:
The diameter in mm (D_mm) of a nozzle as a function of location along the flow direction x_mm have been entered into the Parametric table shown below. The nozzle throat is located at x_mm=4.5 mm. The inlet conditions are 25 C and 2200 kPa. Air_ha (real fluid) is chosen as the gas and a real fluid analysis (Type$='real') is performed. Results are shown in the Parametric table.
$TabStops 0.2 4.5 in
$UnitSystem SI C kPa mass kJ
$Load Component Library
$Varinfo T_in, T_exit Units=C
$VarInfo P_in, P_exit, P_crit, P_design Units=kPa
$VarInfo Vel_in, Vel_exit Units=m/s
$VarInfo A_throat, A_exit, A_s Units=m^2
$VarInfo D_s Units=m
Gas$='air'
D_throat=6.131 [mm]*Convert(mm,m) "throat diameter"
T_in=25 [C] "inlet temperature"
P_in=500 [kPa] "inlet pressure"
Vel_in=1 [m/s] "velocity at nozzle inlet"
A_throat=pi*D_throat^2/4 "critical area"
D_exit=7.015 [mm]*Convert(mm,m) "diameter at nozzle exit"
A_exit=pi*D_exit^2/4 "exit area of nozzle"
D_s_mm=6.63 [mm] "diameter at the location of the normal shock in mm"
D_s=D_s_mm*Convert(mm,m) "diameter at shock location"
A_s=pi*D_s^2/4 "area at the shock location"
CALL CDNozzle2_CL(Gas$,T_in, P_in, Vel_in, A_throat, A_exit, A_s : P_exit, M_exit, T_exit, Vel_exit, P_crit, P_design)
{Solution:
A_exit=0.00003865 [m^2]
A_s=0.00003452 [m^2]
A_throat=0.00002952 [m^2]
D_exit=0.007015 [m]
D_s=0.00663 [m]
D_s_mm=6.63 [mm]
D_throat=0.006131 [m]
Gas$='air'
M_exit=0.5737
P_crit=416.8 [kPa]
P_design=106.1 [kPa]
P_exit=373.2 [kPa]
P_in=500 [kPa]
T_exit=6.59 [C]
T_in=25 [C]
Vel_exit=192.3 [m/s]
Vel_in=1 [m/s]
}
See: CDNozzle1_CL