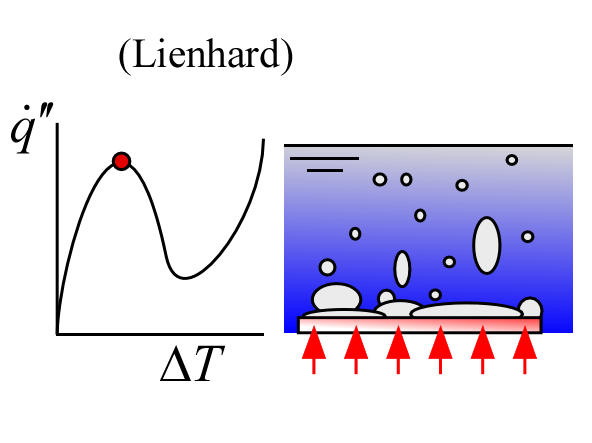
Critical_Heat_Flux_Lienhard

Critical_Heat_Flux_Lienhard returns the critical heat flux in for the specified fluid and geometry using the correlation provided in Eq.7-4 of Nellis and Klein which is based on the work of Lienhard and Dhir (1973)
Inputs:
Fluid$ - a string constant or variable containing the name of a fluid/vapor defined in the EES data base.
Geom$ - a string constant or variable that is one of the following: 'PLATE', 'CYLINDER', 'SPHERE', 'OTHER'
L - the characteristic length [m] or [ft] of the surface. For a sphere or cylinder, L is the radius. For a plate, L is the width. L is not used for "other and C_crit is set to 0.12.
T_sat - saturation temperature of the fluid in [C ], [K], [F], or [R], depending on the setting for the EES unit system
Output:
Critical Heat Flux (i.e., the heat flux at the burnout point) [W/m^2] or [Btu/hr-ft^2]
Example:
Calculate the critical heat flux for R134a at 550 kPa that is heated by a 3.5 cm wide plate.
$UnitSystem SI K kPa J
$TabStops 4 in
$VarInfo q`` units=W/m^2
$VarInfo T_sat units=K
L=0.035 [m] "width of plate"
P=550 [kPa] "pressure of R134a"
T_sat=t_sat(R134a,P=P) "saturation temperature of R134a"
q``=Critical_Heat_Flux('R134a', 'Plate', L, T_sat) "critical heat flux"
{Solution:
q``= 454,766 [W/m^2]}