Nucleate_Boiling_Rohsenow

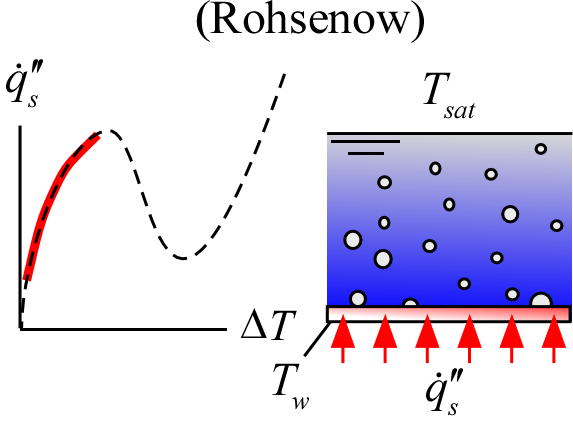
The function Nucleate_Boiling_Rohsenow(Fluid$, T_sat, T_w, C_s_f) returns the surface heat flux for nucleate boiling of a fluid by means of a heated surface of a specified material. This function is presented in Section 7.2.3 of Nellis and Klein and again in Nellis and Klein 2020, Cambridge University Press.
Inputs
Fluid$ - string variable representing a fluid/vapor (i.e., a Real Fluid) in the EES data base.
T_sat - the saturation temperature of the boiling liquid in [C], [K], [F], or [R].
T_w - the temperature of the surface in [C], [K], [F], or [R].
C_s_f - is the surface coefficient which depends on the fluid, surface material and conditions. (Table 7-1 from Nellis and Klein with values for specific situations appears below. If a value of <0 is provided then the default value of 0.013 is used.

Notes:
This procedure is responsible for determining the property data of the specified fluid. It uses the correlation developed by Rohsenow (1952). This function should be used only as a rough estimate of the heat flux as errors of 100% are common. More accurate correlations exist, including the Gorenflo and the Cooper correlations. The Kutateladze correlation is also available in EES as Nucleate_Boiling_Kutateladze.
Example:
$UnitSystem SI C kJ kPa
$VarInfo q``_s units=W/m^2
C_s_f=0.013
T_sat=100 [C]
T_w=105 [C]
Fluid$='Water'
q``_s= nucleate_boiling_rohsenow(Fluid$, T_sat, T_w, C_s_f)
{Solution:
q``_s=17,478 [W/m^2]}