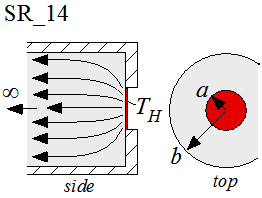
SR_14

Function SR_14(a, b, k) returns the thermal resistance associated with spreading between a circular contact area located on the surface of an infinitely long circular flux tube. The contact area itself is assumed to be exposed to a uniform temperature. The spreading resistance is the thermal resistance that is in addition to the 1-D thermal resistance in the flux tube that would exist if the uniform temperature existed over the entire area of the tube.
Note that if a << b then the result approaches the equivalent result for spreading resistance from a half-space given by SR_1.
Note that the total resistance associated with conduction through a circular bar of length L with a contact on one end will be the sum of the normal, 1D resistance and the spreading resistance:
R_total = L/(k*pi*b^2) + SR_14 (SR_14 only calculates the additional resistance associated with spreading that occurs at the end of the bar)

The calling protocol is:
R = SR_14(a, b, k)
Inputs:
a = radius of contact area [m or ft]
b = radius of flux tube [m or ft]
k = thermal conductivity of the material [W/m-K or Btu/hr-ft-R]
Outputs:
R = spreading resistance [K/W or R-hr/Btu]
Rohsenow, W.M, J. P. Hartnett, and Y. I. Cho, Handbook of Heat Transfer, 3rd Edition, McGraw Hill, (1998).
Example:
$UnitSystem SI Mass J K Pa Radian
$VarInfo R14 units=K/W
a=1 [m]
b=2 [m]
k=1 [W/m-K]
R14=sr_14(a,b,k)
{Solution:
R14 = 0.08491 [K/W]}