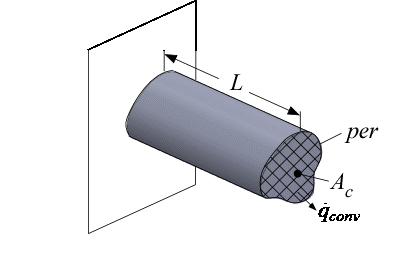
Constant Cross-Section Fin with Tip Convection

Dimensional: eta_fin_constantCS_convtip(A_c, per, L, h, k)
Function eta_fin_constantCS_convtip calculates the fin efficiency of a fin with a constant cross-section and convection from the tip.
The function then calls a corresponding non-dimensional function (see below), which determines the fin efficiency in terms of the fin parameter mL and AR_tip, described below. Note that the area used to define the fin efficiency therefore INCLUDES the tip area (per*L + A_c).
Inputs:
A_c - cross-sectional area [m^2 or ft^2]
per - perimeter [m or ft]
L - length of the fin [m or ft]
h - heat transfer coefficient [W/m^2-K or Btu/hr-ft^2-R]
k - conductivity of fin material [W/m-K or Btu/hr-ft-R]
The units for the inputs to the function are based on the unit setting in EES.
Example:
$UnitSystem SI
h_bar=20 [W/m^2-K]
L=0.1 [m]
A_c=0.001 [m^2]
per=0.01 [m]
k=15 [W/m-K]
eta=eta_fin_constantcs_convtip(A_c, per, L, h_bar, k)
{Solution:
eta=0.8680}
Non-dimensional: eta_fin_constantCS_convtip_ND(mL, AR_tip)
Function eta_fin_constantCS_convtip_ND returns the fin efficiency of a straight fin with a constant cross section given the product of the fin parameter, m, and fin length, L (mL) and the ratio of the tip to side area (AR_tip). These dimensionless parameters are defined as:
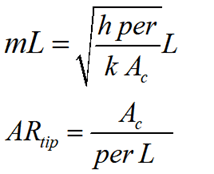
where
A_c - cross-sectional area
per - perimeter
L - length of the fin
h - heat transfer coefficient
k - conductivity of fin material
Note that the area that should be used in conjunction with the calculated fin efficiency must INCLUDE the tip (per*L + A_c).
Example:
mL=1.5 [-]
AR_tip=0.05 [-]
eta=eta_fin_constantcs_convtip_nd(mL, AR_tip)
{Solution:
eta=0.5828}