Contents
- Index
Elevated Temperature Region for Semi-Infinite Body Non-Adjacent to the Adiabatic Surface
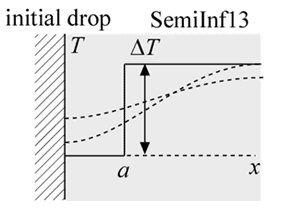
Function semiinf13(T_i, alpha, a, DELTAT, x, time) returns the temperature within a semi-infinite body that has an initial temperature that is non-uniform. The region immediately adjacent to the adiabatic surface (0 < x < a) is at T_i while the remainder of the material (x>a) is elevated by an amount DELTAT. Note that the same result can be obtained by calling the function SemiInf12 with a negative DELTAT.
The calling protocol is:
T = SemiInf13(T_i, alpha, a, DELTAT, x, time)
Inputs:
T_i = temperature adjacent to the surface [C] or [K]
alpha = thermal diffusivity [m^2/s]
a = extent of the reduced temperature region [m]
DELTAT = temperature elevation of the remainder [C] or [K]
x = position relative to surface [m]
time = time relative to beginning of heat flux cycle [s]
This function can be used with English units set in EES. In this case, T_i is in [F] or [R], alpha is in [ft^2/hr], a is in [ft], DELTAK is in [F] or [R], x is in [ft], and time is in [s].
Outputs:
T is the temperature in [C] or [K] (or [F] or [R] in English units)
Carslaw, H.S. and J.C. Jaeger, Conduction of Heat in Solids, 2nd Edition, Oxford, (1959).
Example:
$UnitSystem SI Mass J K Pa Radian
$VarInfo T units=K
T_i=300 [K]
alpha=1e-3 [m^2/s]
x=0.05 [m]
time=0.5 [s]
a=0.005 [m]
DELTAT=100 [K]
T=semiinf13(T_i, alpha, a, DELTAT, x, time)
{Solution:
T=396.4 [K]
}
Transient Conduction Index
