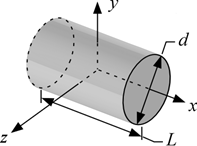
Cylinder

This procedure returns mass and moments of inertia of a cylinder.
Inputs
d = diameter of cylinder [m, ft]
L = length of cylinder [m, ft]
rho = material density [kg/m^3, lbm/ft^3]
Outputs
m=mass [kg, lb_m]
I_x = moment of inertia about the x-axis [kg-m^2 or lbm-ft^2]
I_y= moment of inertia about the y-axis [kg-m^2 or lbm-ft^2]
I_z = moment of inertia about the z-axis [kg-m^2 or lbm-ft^2]
Example:
$Load Mechanical Design
$UnitSystem SI K Pa
$VarInfo I_x units=kg-m^2
$VarInfo I_y units=kg-m^2
$VarInfo I_z units=kg-m^2
d=0.1 [m]
L=0.4 [m]
rho=990 [kg/m^3]
Call moi_cylinder(d, L, rho:m, I_x, I_y, I_z)
{Solution:
I_x=0.003888 [kg-m^2]
I_y=0.04341 [kg-m^2]
I_z=0.04341 [kg-m^2]
}
Reference: Juvinall and Marshek, 5th edition, Fundamentals of Machine Component Design, Appendix B-2