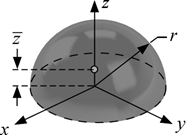
MOI_Hemisphere

This procedure returns mass and moments of inertia of a hemisphere.
Inputs
r = radius of sphere [m, ft]
rho = material density [kg/m^3, lbm/ft^3]
Outputs
m=mass [kg, lb_m]
I_x = moment of inertia about the x-axis [kg-m^2 or lbm-ft^2]
I_y= moment of inertia about the y-axis [kg-m^2 or lbm-ft^2]
I_z = moment of inertia about the z-axis [kg-m^2 or lbm-ft^2]
z_bar = distance from centroid to flat surface [m or ft]
Example:
$Load Mechanical Design
$UnitSystem SI K Pa
$VarInfo I_x units=kg-m^2
$VarInfo I_y units=kg-m^2
$VarInfo I_z units=kg-m^2
r=0.5 [m]
L=0.4 [m]
rho=990 [kg/m^3]
Call moi_hemisphere(r,rho:m, I_x, I_y, I_z, z_bar)
{Solution:
I_x=16.81 [kg-m^2]
I_y=16.81 [kg-m^2]
I_z=25.92 [kg-m^2]
z_bar = 0.1875 [m]
m = 259.2 [kg]
}
Reference: Gray, G.L, F. Costanzo, R.J. Witt, and M.E. Plesha, Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics, Third Edition, McGraw Hill, (2023).