Contents
- Index
K_Gradual_Expansion
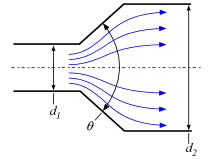
The K_Gradual_Expansion(d_1,d_2, theta) function returns the resistance coefficient for a gradual expansion having the geometry shown in the figure.
The diameters, d_1 and d_2, are expected to be entered in m or ft, depending on the unit system setting in EES.
Note that the resistance coefficient is defined in terms of the velocity in the smaller pipe.
For expansion angles greater than 45 deg, the resistance coefficient is the same as for a sudden expansion.
Example:
$UnitSystem SI K Pa J deg
$VarInfo DELTAP units=Pa
$VarInfo h_L units=m
d_1=0.025 [m]
d_2=0.10 [m]
theta=20[deg]
K=k_gradual_expansion(d_1,d_2,theta)
V_tilde=10 [m/s]
rho=1000 [kg/m^3]
g=g#
h_L=K*V_tilde^2/(2*g)
DELTAP=h_L*rho*g
{Solution:
DELTAP=19841 [Pa]
h_L=2.023 [m]
K=0.3968
}
Notes:
EES determines the minimum and maximum diameters. The maximum diameter is assumed to be d_1 in the figure, but it does not matter if they are switched.
Reference:
Flow of Fluids Through Valves, Fittings, and Pipe, Crane Valves North America, Technical Paper No. 410M. 1979
Minor Losses Index
