FUGACITY
The FUGACITY function returns the fugacity of the specified pure fluid for the given conditions. Fugacity is defined by the following relation:
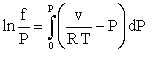
where
f is fugacity (same units as pressure)
P is pressure
v is the specific volume of the fluid
T is the absolute temperature
R is the gas constant.
For an ideal gas fluid, f is identical to P.
The FUGACITY function will accept any appropriate set of inputs. Fugacity is particularly useful for some types of phase equilibrium calculations.
Example:
R$='Argon'
$UnitSystem SI K kPa
$VarInfo f units=kPa
f=Fugacity(R$,T=100 [K],P=101.3 [kPa])
{Solution: f=99.04 kPa}
Return to Thermophysical Functions