Calling EES from Python
Python can call EES (version12.131 or newer) to:
em_Solve: Solve the program in an open EES application
em_RunMacroTab: Run a macro from a specified tab in the Macro window in an open EES application
Input information must be provided to EES from Python. This is done by Python writing text files that EES can import. Then EES exports calculated results that Python imports.
The communication between Python and EES relies on functions FindWindow and SendMessage in the Windows operating system and is quite fast. EES writes a file named EESCallfromApp.log in the EES directory that records all of the communications and error messages.
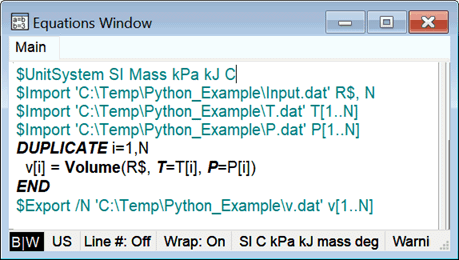
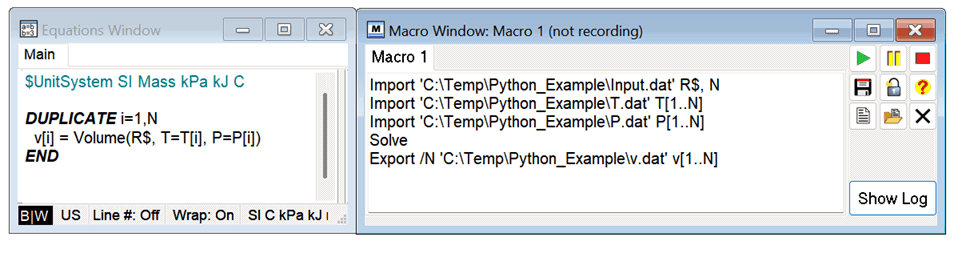
A simple example is used here to illustrate all of the options in the Python-EES communication. Python writes the name of a refrigerant (R$) and number of data points (N) in file Input.dat along with arrays of N temperatures and pressures in files T.dat and P.dat. When called from Python, EES reads these files with its $Import directive or Import macro command. EES uses the temperature and pressures to calculate an array of specific volumes, which are exported using the $Export directive or Export macro command to file v.dat. Python waits for EES to complete the calculations and then imports file v.dat. It should be understood that Python and EES can be modified to exchange any desired information in any number of files .
The EES program used in the example for the em_Solve command is:

The EES program and Macro used in the example for the em_RunMacroTab command is:
The Python code follows. Comments in green font indicate the purpose of each function and explain how to use the program. Note that the exporttoEES and importEESFile functions will need be modified for other problems.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
import win32api
import win32con
import win32gui
import time
import sys
import numpy as np
import os
import subprocess
em_DeleteLog=0
em_StopLog=1
em_StartLog=2
em_Solve=10
em_RunMacroTab=20
em_TerminateEES=100
wm_RunEES=32777
notUsed=0
def exporttoEES():
#The user needs to write the files here that EES will import.
Refrig='R134a'
N=12
T=[10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120]
P=[20,20,20,20,20,20,20,20,20,20,20,20]
with open('c:/temp/Python_Example/Input.dat',"w") as file:
file.write(str(Refrig)+"\n")
file.write(str(N)+"\n")
np.savetxt('c:/temp/Python_Example/T.dat',T)
np.savetxt('c:/temp/Python_Example/P.dat',P)
return
def importEESFile(filename):
#The user needs to write this file to import the results exported by EES
if (not os.path.exists(filename)):
print(f"Output file "+filename+" was not found")
else:
v=np.loadtxt(filename) #load the array of specific volumes for this example
print(v) #print the results to verify that they were correctly imported from EES in this example
return
# Find an running instance of EES and return the window handle
def find_window():
EESClass="TEES_D"
try:
hwnd = win32gui.FindWindow(EESClass, None)
return hwnd
except win32api.error:
return None
def StopLog_EES(hwnd):
#Send EES a message to stop logging to EESCallFromApp.log and delete the log file
win32gui.SendMessage(hwnd,wm_RunEES,em_StopLog,notused)
return
def StartLog_EES(hwnd):
# Send EES a message to start logging to EESCallFromApp.log in the EES folder; The log file will be created if it does not exist.
win32gui.SendMessage(hwnd,wm_RunEES,em_StartLog,notused)
return
def Solve_EES(hwnd):
#Solve a previously-opened EES program. Use $Import and $Export in EES to read/write text files
errcode = win32gui.SendMessage(hwnd,wm_RunEES,em_Solve,notUsed)
return errcode
def solve_EESMacroTab(hwnd,TabNo):
#Solve macro file TabNo in the macro window of an open EES program.
errcode = win32gui.SendMessage(hwnd,wm_RunEES,em_RunMacroTab,TabNo)
return errcode
def wait_for_file(file_path, timeout=60, check_interval=1):
#Waits for a file to exist at the given path: Needed only when starting EES with the em_RunMacroName command.
start_time = time.time()
while not os.path.exists(file_path):
if time.time() - start_time > timeout:
# print(f"Timeout: File '{file_path}' did not appear within {timeout} seconds.")
return False
time.sleep(check_interval)
return True
if __name__ == "__main__":
exporttoEES #write text files that EES or an EES macro will import
vfile='c:/temp/Python_Example/v.dat' #name of file written by EES that will be imported
EESFolder='C:/EES32' #folder containing the EES application
logfile=EESFolder+'/EESCallFromApp.log' #name of the log file
try:
os.remove(vfile) #delete existing output file
except:
x=1 #do nothing
try:
os.remove(logfile) #delete existing log file
except:
x=1 #do nothing
hwnd = find_window() #find the handle of the open EES application
while True:
EESCode=input("Enter: em_DeleteLog em_StopLog, em_StartLog, em_Solve, EM_RunMacroTab or Quit: ")
match EESCode:
case 'em_DeleteLog':
if (os.path.exists(logfile)):
os.remove(logFile)
print(f"File "+logfile+" has been deleted")
case 'em_StopLog':
print(f"EM_StopLog: Stop logging to "+logfile)
if hwnd:
StopLog_EES(hwnd)
case 'em_StartLog':
print(f"EM:StartLog: Clear log and start logging to "+logfile)
if hwnd:
StartLog_EES(hwnd)
case 'em_Solve':
if hwnd:
print(f"Solving the currently open EES file using the Solve command")
errcode=Solve_EES(hwnd)
if errcode==0:
importEESFile(vfile)
else:
print(f"Error #"+str(errcode)+". The error message is shown in file EESCallFromApp.log in the EES directory.")
else:
print(f"Start EES and open the EES file that is to be solved")
case 'em_RunMacroTab':
TabNo=1 #the tab number in the EES Macro window that will be run. The first tab is 1
if hwnd:
errcode=solve_EESMacroTab(hwnd,TabNo)
if errcode==0:
importEESFile(vfile)
else:
print(f"Error #"+str(errcode)+". The error message is shown in file EESCallFromApp.log in the EES directory.")
else:
print(f"Start EES and open the EES file that has the macro file that is to be solved")
case 'em_TerminateEES': #closes the open EES application
subprocess.call(["taskkill", "/IM", "EES.exe", "/F"])
case 'Quit':
print(f"Quitting EES calls")
break
case _:
print (f"Input not recognized - try again")
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
To continue with this example, start EES and enter the small program shown in the first figure for the em_Solve command. Save the file in C:\temp\Python_Example\em_Solve.ees. Next copy the Python program listing above into Python and run it. Python will prompt you for a command. Enter em_Solve. You should then see the calculated specific volumes as shown below. Enter Quit to exit the Python program.
Enter: em_DeleteLog em_StopLog, em_StartLog, em_Solve, EM_RunMacroTab or Quit: em_Solve
Solving the currently open EES file using the Solve command
[1.1480915 1.18933484 1.23051515 1.27164302 1.31272684 1.35377334
1.394788 1.43577531 1.476739 1.51768217 1.55860743 1.59951699]
Enter: em_DeleteLog em_StopLog, em_StartLog, em_Solve, EM_RunMacroTab or Quit: Quit
Quitting EES calls
See also: Call Python from EES