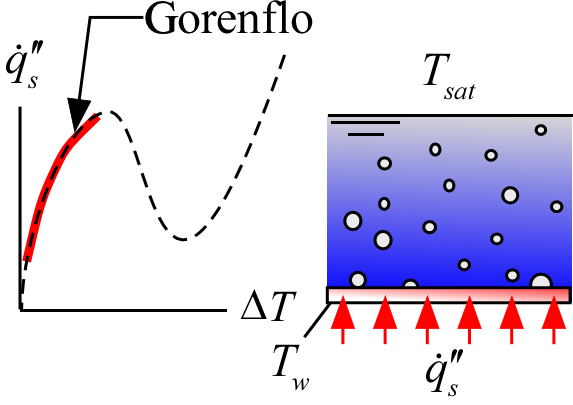
Nucleate_Boiling_Gorenflo

The function Nucleate_Boiling_Gorenflo(Fluid$, T_sat, T_w, R_p, H_0) returns the surface heat flux for nucleate boiling of a fluid. This correlation is presented in Chapter 11 of Ghiaasiaan (2008) and is based on the work of Leiner and Gorenflo (1992).
Inputs
Fluid$ - string variable representing a fluid/vapor (i.e., a Real Fluid) in the EES data base.
T_sat - the saturation temperature of the boiling liquid in [C], [K], [F], or [R].
T_w - the temperature of the surface in [C], [K], [F], or [R].
R_p - surface roughness [m] or [ft]. If R_p<0 then the default value of R_p is used (R_p = 0.4 micron).
H_0 - reference heat transfer coefficient [W/m^2-K] or [Btu/hr-ft^2-R]. H_0 is the reference heat transfer coefficient corresponding to a reference heat flux of q``_0 = 20000 W/m^2 at a reduced pressure (pressure/critical pressure) of 0.1. If H_0<0 then a default value is used - this default value of H_0 for many fluids are tabulated and included in the function. If the fluid is not in this list then the Cooper correlation is used to estimate H_0.
Notes:
This procedure is responsible for determining the property data of the specified fluid and implementing the correlation. The Kutateladze correlation is also available in EES as Nucleate_Boiling_Kutateladze. The Rohsenow and Cooper correlations are also available.
Example:
$UnitSystem SI Mass J Pa K
$VarInfo q``_s Units = 'W/m^2'
Fluid$ = 'Water'
P = 1 [atm]*Convert(atm,Pa)
DT = 10 [K]
T_sat = T_sat(Fluid$,P=P)
T_w = T_sat + DT
q``_s = Nucleate_Boiling_Gorenflo(Fluid$,T_sat, T_w, -999 [m], -999 [W/m^2-K])
{Solution:
q``_s=34077 [W/m^2]}