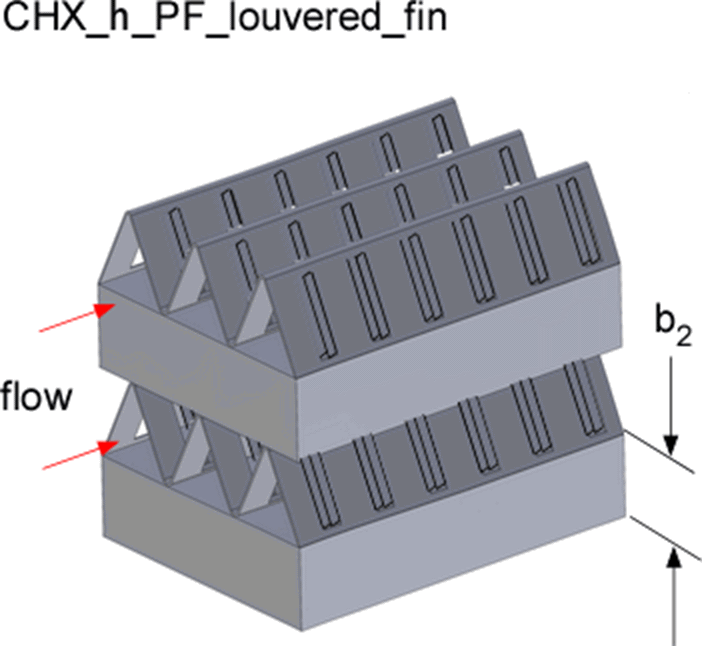
PF louvered-fin h

The procedure:
CHX_h_PF_Louvered_Fin(TypeHX$, m_dot, A_fr_tot, b_2, Fluid$, T, P:h)
provides the heat transfer coefficient associated with a louvered-fin compact heat exchanger surface. These data are from Kays and London (1994).
Inputs
TypeHX$: string identifying the geometry
3/8-6.06: 'PF_louvered-fin_38_606'
3/8(a)-6.06: 'PF_louvered-fin_38a_606'
1/2-6.06: 'PF_louvered-fin_12_606'
1/2(a)-6.06: 'PF_louvered-fin_12a_606'
3/8-8.7: 'PF_louvered-fin_38_87'
3/8(a)-8.7: 'PF_louvered-fin_38a_87'
3/16-11.1: 'PF_louvered-fin_316_111'
1/4-11.1: 'PF_louvered-fin_14_111'
1/4(b)-11.1: 'PF_louvered-fin_14b_111'
3/8-11.1: 'PF_louvered-fin_38_111'
3/8(b)-11.1: 'PF_louvered-fin_38b_111'
1/2-11.1: 'PF_louvered-fin_12_111'
3/4-11.1: 'PF_louvered-fin_34_111'
3/4(b)-11.1: 'PF_louvered-fin_34b_111'
m_dot: mass flow rate (kg/s or lbm/hr)
A_fr_tot: total frontal area as viewed by the flow approaching the tube bank (m^2 or ft^2); note that this includes both the louvered fin channels and the space occupied by the other channels
b_2: the width between adjacent pin fin channels occupied by the other channels (m or ft)
Fluid$: string indicating the fluid type
T: temperature of the fluid (K, C, R, or F)
P: absolute pressure of the fluid (Pa, kPa, bar. MPa, atm, or psi)
Output
h: heat transfer coefficient (W/m^2-K or Btu/hr-ft^2-R) averaged over entire louvered fin surface (includes plates)
Example
$UnitSystem SI Mass J K Pa
$VarInfo h units=W/m^2-K
TypeHX$='PF_louvered-fin_38_606'
m_dot=0.7 [kg/s]
A_fr_tot=0.5 [m^2]
L=0.1 [m]
Fluid$='Air'
T=300 [K]
T_i=300 [K]
T_o=300 [K]
P=101325 [Pa]
b_2=0.01 [m]
CALL CHX_H_PF_Louvered_Fin('PF_louvered-fin_12a_606', m_dot, A_fr_tot, b_2, Fluid$, T, P:h)
{Solution:
h = 57.13 [W/m^2-K]}
Related procedures include: